Nöroşirürjide cerrahi mikroskopların uygulama tarihi ve rolü
Nöroşirürji tarihinde,cerrahi mikroskoplarGeleneksel nöroşirürji çağının çıplak gözle ameliyat yaptığı dönemden, modern nöroşirürji çağının çıplak gözle ameliyat yaptığı döneme geçişi sağlayan çığır açıcı bir semboldür.mikroskop. Kim ve ne zaman yaptı?ameliyat mikroskoplarıNöroşirürjide kullanılmaya başlanmasının rolü nedir?cerrahi mikroskopNöroşirürjinin gelişiminde rol oynadı mı? Bilim ve teknolojinin ilerlemesiyle birlikte,Ameliyat mikroskobuDaha gelişmiş ekipmanlarla değiştirilebilir mi? Bu, her beyin cerrahının bilmesi gereken bir sorudur ve beyin cerrahisi alanındaki en son teknoloji ve cihazları uygulayarak beyin cerrahisi becerilerinin gelişimini desteklemelidir.
1、Tıbbi Alanda Mikroskopi Uygulamalarının Tarihi
Fizikte gözlük camları, tek bir yapıya sahip, büyüteç etkisi yaratan ve büyütme gücü sınırlı olan dışbükey merceklerdir; bunlara büyüteç denir. 1590 yılında iki Hollandalı, ince silindirik bir namlunun içine iki dışbükey mercek plakası yerleştirerek dünyanın ilk kompozit yapıdaki büyüteç cihazını icat etti:mikroskopDaha sonra mikroskobun yapısı sürekli olarak geliştirildi ve büyütme oranı sürekli olarak artırıldı. O dönemde bilim insanları çoğunlukla bu yöntemi kullanıyordu.kompozit mikroskopHücre yapısı gibi hayvan ve bitkilerin minik yapılarını gözlemlemek için. 19. yüzyılın ortalarından sonlarına doğru, büyüteçler ve mikroskoplar tıp alanında kademeli olarak kullanılmaya başlandı. İlk başlarda cerrahlar, ameliyatlarda burun köprüsüne yerleştirilebilen tek mercekli gözlük camı tipi büyüteçler kullandılar. 1876'da Alman doktor Saemisch, bileşik bir gözlük camı büyüteci kullanarak dünyanın ilk "mikroskopik" ameliyatını gerçekleştirdi (ameliyat türü bilinmiyor). 1893'te Alman şirketi Zeiss,binoküler mikroskop, esas olarak tıbbi laboratuvarlarda deneysel gözlem ve oftalmoloji alanında kornea ve ön oda lezyonlarının gözlemlenmesi için kullanılır. 1921'de, hayvanların iç kulak anatomisi üzerine laboratuvar araştırmalarına dayanarak, İsveçli kulak burun boğaz uzmanı Nylen sabit birmonoküler cerrahi mikroskopİnsanlarda kronik orta kulak iltihabı ameliyatı gerçekleştirmek için kendisi tarafından tasarlanıp üretildi; bu gerçek bir mikrocerrahiydi. Bir yıl sonra, Nylen'in baş doktoru Hlolmgren,binoküler cerrahi mikroskobuZeiss tarafından ameliyathanede üretilmiştir.
ErkenAmeliyat mikroskoplarıZayıf mekanik stabilite, hareket edememe, farklı eksenlerin aydınlatılması ve objektif merceğinin ısınması, dar cerrahi büyütme alanı vb. gibi birçok dezavantajı vardı. Bunların hepsi, daha geniş uygulama alanını sınırlayan nedenlerdir.cerrahi mikroskoplarSonraki otuz yılda cerrahlar ve cerrahlar arasındaki olumlu etkileşim sayesindemikroskop üreticileri, performansıcerrahi mikroskoplarsürekli olarak iyileştirildi vebinoküler cerrahi mikroskopları, çatıya monte mikroskoplar, zum lensler, koaksiyel ışık kaynağı aydınlatması, elektronik veya su basıncıyla kontrol edilen eklemli kollar, ayak pedalı kontrolü vb. ardışık olarak geliştirildi. 1953 yılında Alman şirketi Zeiss, bir dizi özel ürün üretti.otoloji için cerrahi mikroskoplarÖzellikle orta kulak ve temporal kemik gibi derin lezyonların ameliyatları için uygundur.cerrahi mikroskoplarGelişmeye devam ettikçe, cerrahların zihniyeti de sürekli değişiyor. Örneğin, Alman doktorlar Zollner ve Wullstein,cerrahi mikroskoplarTimpanik membran şekillendirme cerrahisinde kullanılması zorunludur. 1950'lerden bu yana, göz doktorları oftalmik muayenelerde yalnızca mikroskop kullanma uygulamasını kademeli olarak değiştirmiş veotocerrahi mikroskoplarıgöz cerrahisine girdi. O zamandan beri,Ameliyat mikroskobuOtoloji ve oftalmoloji alanlarında yaygın olarak kullanılmaktadır.
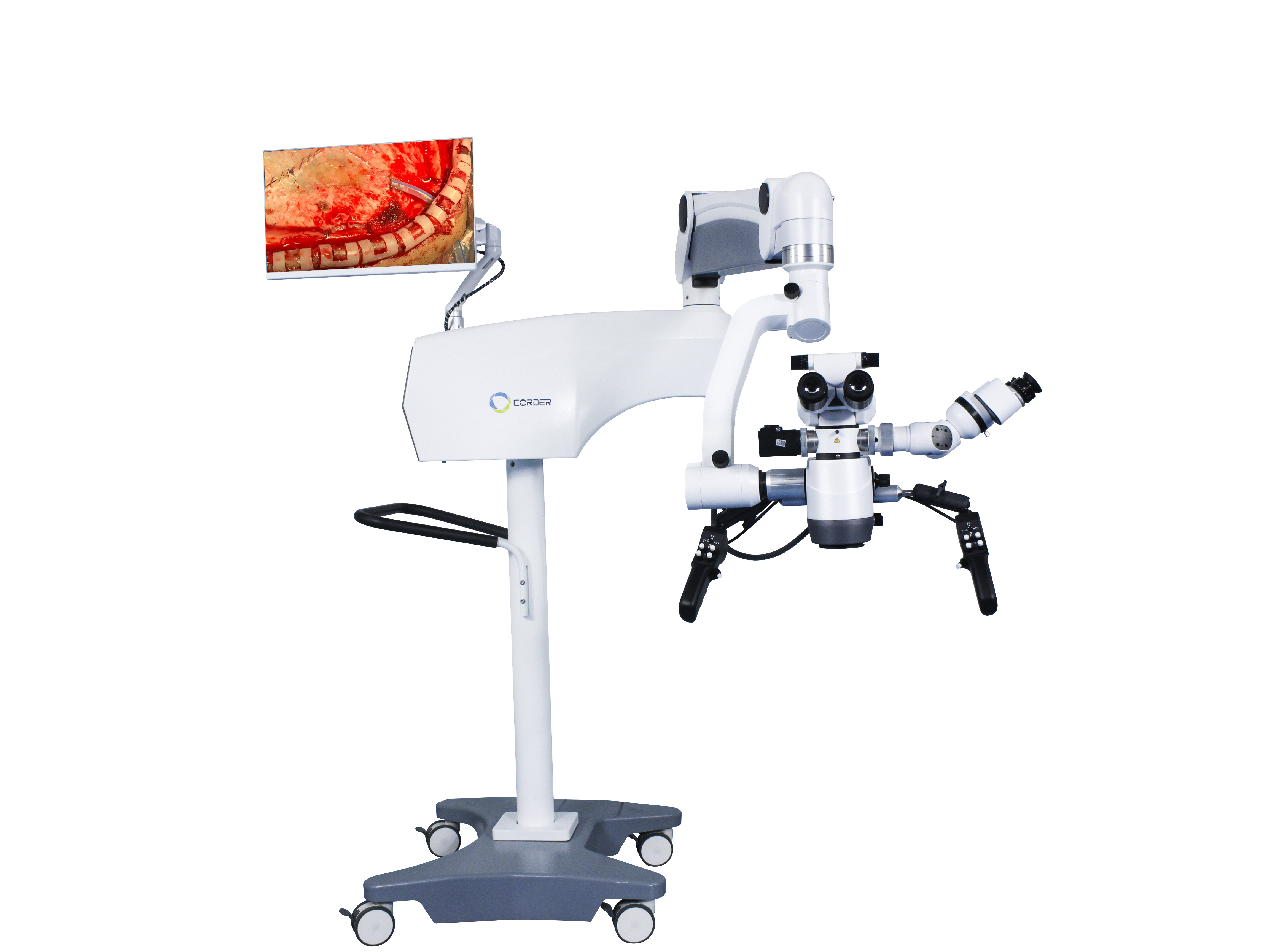
2、Nöroşirürjide cerrahi mikroskobun uygulanması
Nöroşirürjinin özelliğinden dolayı, uygulanmasınöroşirürjide cerrahi mikroskoplarotoloji ve oftalmolojiden biraz daha geç bir dönemdedir ve beyin cerrahları bu yeni teknolojiyi aktif olarak öğrenmektedir. O dönemde,cerrahi mikroskopların kullanımıçoğunlukla Avrupa'daydı. Amerikalı göz doktoru Perrit ilk olarakcerrahi mikroskoplar1946'da Avrupa'dan Amerika Birleşik Devletleri'ne taşınarak, Amerikalı beyin cerrahlarının bu yöntemi kullanmasının temelleri atıldıAmeliyat mikroskopları.
İnsan hayatının değerine saygı açısından, insan vücudu için kullanılan her yeni teknoloji, ekipman veya alet, ön hayvan deneylerinden ve operatörler için teknik eğitimden geçmelidir. 1955 yılında Amerikalı beyin cerrahı Malis, bir beyin cerrahisi cihazı kullanarak hayvanlar üzerinde beyin ameliyatı gerçekleştirdi.binoküler cerrahi mikroskobuAmerika Birleşik Devletleri'ndeki Güney Kaliforniya Üniversitesi'nde beyin cerrahı olan Kurze, mikroskop altında kulak ameliyatlarını gözlemledikten sonra laboratuvarda bir yıl boyunca mikroskop kullanmanın cerrahi tekniklerini öğrendi. Ağustos 1957'de, 5 yaşında bir çocuğa akustik nöroma ameliyatını başarıyla gerçekleştirdi.kulak ameliyatı mikroskobuDünyanın ilk mikrocerrahi ameliyatıydı. Kısa bir süre sonra Kurze, bir çocukta yüz siniri dil altı sinir anastomozunu başarıyla gerçekleştirdi.cerrahi mikroskopve çocuğun iyileşmesi mükemmel oldu. Bu, dünyadaki ikinci mikrocerrahi ameliyattı. Kurze daha sonra, çocukları taşımak için kamyonlar kullandı.Ameliyat mikroskoplarıMikrocerrahi nöroşirürji için çeşitli yerlere gitti ve şiddetle tavsiye etticerrahi mikroskoplarDiğer beyin cerrahlarına. Daha sonra Kurze, bir beyin anevrizması klipleme ameliyatı gerçekleştirdi.cerrahi mikroskop(Maalesef herhangi bir makale yayınlamadı). Tedavi ettiği bir trigeminal nevralji hastasının desteğiyle, 1961 yılında dünyanın ilk mikro kafa tabanı nöroşirurji laboratuvarını kurdu. Kurze'nin mikrocerrahiye katkılarını her zaman hatırlamalı ve yeni teknolojileri ve fikirleri kabul etme cesaretinden ders çıkarmalıyız. Ancak, 1990'ların başına kadar Çin'deki bazı beyin cerrahları bu yeniliği kabul etmedi.Nöroşirürji mikroskoplarıAmeliyat için. Bu bir sorun değildiNöroşirürji mikroskobukendisi değil, beyin cerrahlarının ideolojik anlayışındaki bir sorundur.
1958'de Amerikalı beyin cerrahı Donaghy, Burlington, Vermont'ta dünyanın ilk mikrocerrahi araştırma ve eğitim laboratuvarını kurdu. İlk aşamalarda, üstlerinin kafa karışıklığı ve maddi sıkıntılarıyla da karşılaştı. Akademisyenlik kariyeri boyunca, beyin trombozu olan hastalardan doğrudan trombüs çıkarmak için kortikal kan damarlarını kesmeyi hep hayal etmişti. Bu nedenle, hayvan ve klinik araştırmalarda damar cerrahı Jacobson ile iş birliği yaptı. O dönemde, çıplak gözle görülebilen koşullar altında, yalnızca çapı 7-8 milimetre veya daha büyük olan küçük kan damarları dikilebiliyordu. Daha ince kan damarlarının uçtan uca anastomozunu sağlamak için Jacobson, ilk olarak gözlük tipi bir büyüteç kullanmayı denedi. Kısa süre sonra,kulak burun boğaz cerrahi mikroskobuAsistan hekim olarak çalıştığı dönemde cerrahi müdahale için. Bu nedenle, Almanya'daki Zeiss'ın yardımıyla Jacobson, çift operatörlü bir cerrahi mikroskop tasarladı (Diploskop) vasküler anastomoz için, iki cerrahın aynı anda ameliyat yapmasına olanak tanıyan bir yöntemdir. Kapsamlı hayvan deneylerinin ardından Jacobson, köpekler ve karotis dışı arterlerin mikrocerrahi anastomozunu konu alan ve %100 vasküler anastomoz açıklığı oranına sahip bir makale yayınladı (1960). Bu, mikrocerrahi nöroşirurji ve vasküler cerrahi ile ilgili çığır açan bir tıbbi makaledir. Jacobson ayrıca mikro makas, mikro iğne tutucular ve mikro alet sapları gibi birçok mikrocerrahi alet tasarlamıştır. 1960 yılında Donaghy, bir beyin arteri kesisi trombektomisini başarıyla gerçekleştirdi.cerrahi mikroskopBeyin trombozu olan bir hasta için. Amerika Birleşik Devletleri'nden Rhoton, 1967'de mikroskop altında beyin anatomisini incelemeye başlayarak mikrocerrahi anatomi alanında yeni bir çığır açtı ve mikrocerrahinin gelişimine önemli katkılarda bulundu.cerrahi mikroskoplarve mikrocerrahi aletlerin gelişmesiyle birlikte, giderek daha fazla cerrah bu aletleri kullanmayı tercih ediyorcerrahi mikroskoplarcerrahi için. Ve mikrocerrahi prosedürlerle ilgili birçok makale yayınladı.
3、Çin'de nöroşirürjide cerrahi mikroskobun uygulanması
Japonya'da yaşayan vatansever bir Çinli olan Profesör Du Ziwei, ilk yerli malı bağışladınöroşirürjik mikroskopve ilgilimikrocerrahi aletler1972 yılında Suzhou Tıp Fakültesi Bağlı Hastanesi'nin (şimdiki adıyla Suzhou Üniversitesi Bağlı Birinci Hastanesi'nin Nöroşirürji Bölümü) Nöroşirürji Bölümü'ne başvurdu. Çin'e döndükten sonra, ilk olarak intrakraniyal anevrizmalar ve menenjiyomlar gibi mikrocerrahi ameliyatlar gerçekleştirdi.nöroşirürjik mikroskoplarve mikrocerrahi aletleri, Pekin Yiwu Hastanesi Nöroşirürji Bölümü'nden Profesör Zhao Yadu, Suzhou Tıp Fakültesi'nden Profesör Du Ziwei'yi ziyaret ederek aletlerin kullanımını gözlemledi.cerrahi mikroskoplarŞanghay Huashan Hastanesi'nden Profesör Shi Yuquan, mikrocerrahi prosedürleri gözlemlemek için Profesör Du Ziwei'nin bölümünü bizzat ziyaret etti. Sonuç olarak, bir tanıtım, öğrenme ve uygulama dalgası yaşandı.Nöroşirürji mikroskoplarıÇin'deki büyük nöroşirurji merkezlerinde başlatılan ve Çin'de mikro nöroşirurjinin başlangıcını işaret eden bir girişimdir.
4、Mikrocerrahi Cerrahisinin Etkisi
Kullanımı nedeniylenöroşirürjik mikroskoplarÇıplak gözle yapılamayan ameliyatlar, 6-10 kat büyütme koşulları altında uygulanabilir hale gelir. Örneğin, etmoid sinüs yoluyla hipofiz tümörü ameliyatı yapmak, normal hipofiz bezini korurken hipofiz tümörlerini güvenli bir şekilde tespit edip çıkarabilir; çıplak gözle yapılamayan ameliyatlar, beyin sapı tümörleri ve omurilik intramedüller tümörleri gibi daha iyi ameliyatlar haline gelebilir. Akademisyen Wang Zhongcheng, beyin anevrizması ameliyatından önce %10,7'lik bir ölüm oranına sahipti.nöroşirürji mikroskobu1978'de mikroskop kullanılmaya başlandıktan sonra ölüm oranı %3,2'ye düştü. Serebral arteriovenöz malformasyon cerrahisinde mikroskop kullanılmadan yapılan ölüm oranı %3,2'dir.cerrahi mikroskop%6,2 idi ve 1984'ten sonra, birnöroşirürji mikroskopları, ölüm oranı %1,6'ya düştü.nöroşirürji mikroskobuHipofiz tümörlerinin kraniotomiye gerek kalmadan minimal invaziv transnazal transsfenoidal yaklaşımla tedavi edilmesine olanak tanır ve cerrahi mortalite oranını %4,7'den %0,9'a düşürür. Bu sonuçlara geleneksel brüt göz cerrahisinde ulaşmak imkansızdır, bu nedenlecerrahi mikroskoplarModern nöroşirurjinin simgesi haline gelmiş olup, modern nöroşirurjinin vazgeçilmez ve yeri doldurulamaz cerrahi ekipmanlarından biri haline gelmiştir.
Gönderi zamanı: 09-12-2024